Trusted and Accurate Bottleneck Calculator
Last Updated (Jan 2026): Dear Visitor, we have recently added the latest CPU and GPU models of this year to our bottleneck calculator. If you would like to see bottleneck analysis for any newly released hardware, feel free to contact us.
Core Features of Our PC Bottleneck Calculator
Why Choose Us
What is Bottleneck Calculator?
A bottleneck calculator is a free online tool that analyzes the interaction between key hardware components, particularly the CPU (central processing unit) and GPU (graphics processing unit). Based on a complex algorithm, our bottleneck calculator evaluates the performance of the CPU, GPU, and RAM to determine which component may be limiting the overall speed and efficiency of your system. This helps users identify potential bottlenecks and make informed decisions to optimize their PC performance even without upgrading hardware.
This tool is especially made for professional gamers, who play high-end games like Red Dead Redemption 2, God of War, Cyberpunk 2077, racing spectacles like Forza Horizon 5, and Microsoft Flight Simulator, and for people who do heavy multitasking, like video editing, 3D rendering, or running multiple applications at once. During these intense sessions, they often face problems such as FPS drops, system lag, and slow response times. For solutions to all these problems, be sure to use our trusted tool. For your convenience, we’ve explained the full method in the video below, showing exactly how you can use the bottleneck calculator.
How to Interpret Bottleneck Calculator Results?
Start by selecting your CPU (Central Processing Unit), GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), and RAM (Random Access Memory). These are primary components for bottleneck detection. For more accurate analysis, you can also select additional factors like RAM, Windows version, storage type, resolution, use case, and operating system architecture. The more accurate your inputs, the more precise your results will be.
Once all fields are set, click “Calculate Bottleneck.” Our bottleneck calculator instantly processes your inputs and provides an overall performance analysis of your entire PC. It uses an advanced calculation mechanism based on component benchmark scores for reliable results.
Performance Analysis
At the top of your results, you’ll see a quick snapshot of how balanced your system is. A simple status label, such as No Bottleneck Detected, Moderate Bottleneck, or Bottleneck Detected, makes it easy to understand performance at a glance.



Below, you’ll see a percentage-based bottleneck ratio indicating how much one component is limiting the other’s performance, and the system health score representing the overall stability and performance efficiency of your pc. Furthermore, there is a general use analysis section which provides a summary of your system’s performance, capabilities, and suggests quick upgrades to prevent your PC from bottlenecks. If you selected a primary use case, this summary will be tailored to match that specific scenario (e.g., gaming, editing, or productivity).
Utilization Insights
This section contains the visual representation of the usage levels of CPU, GPU, and RAM. These visualizations illustrate the efficiency of each system component. Clicking on any graph expands it into a more detailed breakdown, revealing hidden performance trends and helping you pinpoint where slowdowns occur.
Comparison Section
The comparison chart places your CPU and GPU side by side, highlighting how well they complement each other. A large performance gap usually signals a mismatch that could be causing bottlenecks. This insight helps you decide whether a CPU or GPU upgrade will deliver the most noticeable performance boost.
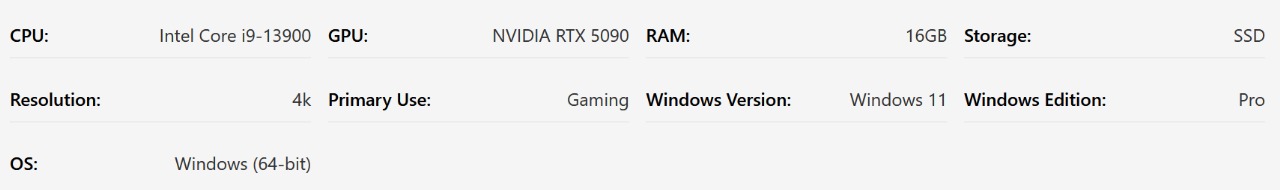
System Information
The System Info section shows a clear summary of the components and settings you selected for the analysis. Double-checking this data ensures your results are accurate and relevant. Even a small error in component selection can lead to misleading conclusions.
Optimization & Upgrade Recommendations
Finally, in this section, you will get the solution to your problems and learn how to resolve the bottleneck in your system. The advice is further divided into three portions, like…

Real-Life Example
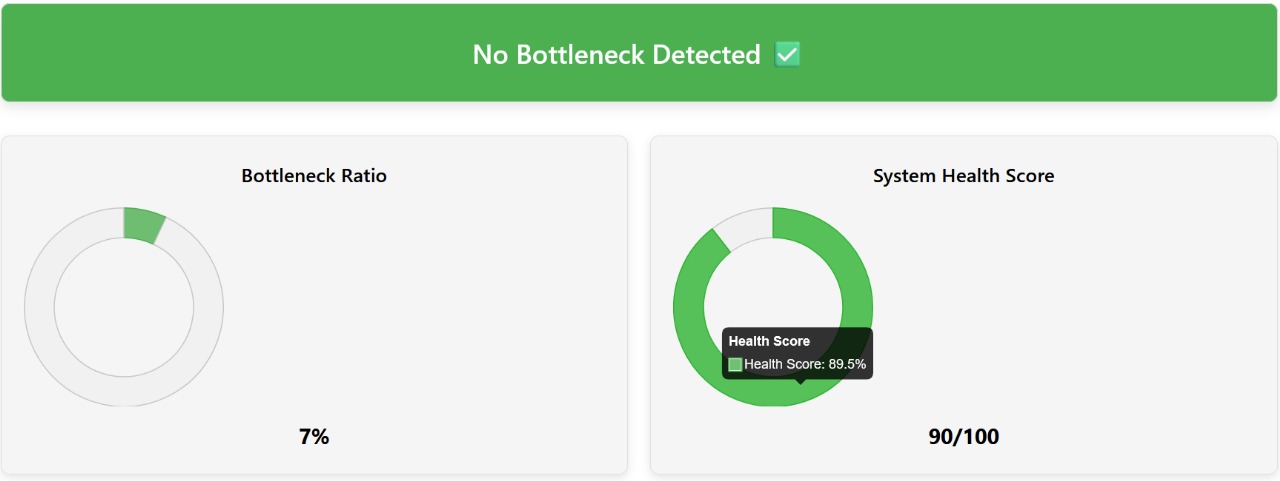
My friend Irfan, who is a professional gamer, was playing top 4K games like Red Dead Redemption 2 on high settings, but he was experiencing FPS drops and occasional lag. He told me that there might be a problem with his PC, so I asked him to try our bottleneck calculator. He selected his hardware components in the calculator, such as an Intel Core i3-13100 CPU and an NVIDIA GTX 980 GPU, and the results showed a 42% severe bottleneck. In the performance analysis section of our tool, it indicated that both the CPU and GPU were mismatched and affecting each other’s performance.



In the Optimization & Upgrades section of the bottleneck calculator, the tool recommended upgrading his hardware to an Intel Core i7-13700K CPU and an NVIDIA RTX 4080 GPU. After upgrading these components, he recalculated his system, and the results showed a 99% system health with only a 1% bottleneck.
He then played the same game on ultra settings, and all the issues he previously faced—FPS drops and lag—had disappeared. Now, he could multitask on his PC, enjoy smooth gameplay, and handle heavy workloads efficiently.


This example demonstrates how he resolved the bottlenecking issue on his PC by following smart recommendations provided by our calculator. With just a few clicks, our calculator identifies performance issues and suggests practical solutions to fix them, saving you time & money.
What is PC Bottleneck?
A PC bottleneck refers to a situation where one component in your system slows down the performance of another or prevents your PC from running at its full potential. It’s not always about the age or quality of your parts; sometimes, even brand-new hardware can hold each other back if they aren’t balanced.
Signs of PC Bottleneck
Causes of PC Bottleneck
Types of Bottlenecks
1. CPU Bottleneck
A CPU bottleneck occurs when the processor cannot keep up with the demands of the system, especially the graphics card. When the CPU is too slow to process calculations or deliver instructions on time, the GPU is forced to wait instead of operating at full capacity. This results in issues such as lower frame rates, stuttering, input lag, and inconsistent performance, even if you’re using a powerful GPU. Our trusted bottleneck calculator will help you identify such CPU limitations precisely and provide upgrade suggestions for balanced performance.
Signs of a CPU bottleneck
For example, switching tabs while gaming takes too much time, taking more than one second to register a button press. These are common signs that your CPU is under stress.
CPU Bottleneck Causes and Solutions
| Cause | Why It Creates a Bottleneck | Recommended Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low Core / Thread Count | Modern games and multitasking workloads rely on parallel processing; fewer cores and threads struggle to handle simultaneous tasks. | Upgrade to a modern CPU with at least 6 cores and 12 threads for balanced performance. |
| Low Clock Speeds or Weak IPC | Low clock speeds or poor instructions-per-clock (IPC) limit performance in CPU-intensive tasks. | Choose a CPU with strong single-core performance and higher IPC instead of relying only on overclocking. |
| Small CPU Cache | Limited cache increases memory access latency, reducing efficiency in games and productivity workloads. | Upgrade to a newer CPU architecture with a larger and faster L3 cache. |
| Thermal Throttling | Poor cooling causes the CPU to reduce clock speeds to prevent overheating. | Improve cooling with better airflow, quality CPU coolers, and proper thermal paste. |
| Excessive Background Processes | Background applications consume CPU resources needed for active workloads. | Disable unnecessary startup programs and close unused background apps. |
2. GPU Bottleneck
A graphics card is designed for parallel processing, meaning it has hundreds or even thousands of small cores (shaders) that can handle many calculations at the same time. This makes it ideal for rendering 3D graphics, textures, and visual effects, as well as performing repetitive calculations in fields like AI, machine learning, and scientific simulations. GPUs also have their own high-speed VRAM to store large textures, models, and datasets, which helps them run intensive applications smoothly.
The CPU sends instructions to the GPU, and the GPU executes them rapidly in parallel. If the GPU can’t keep up with these instructions, due to its few cores, insufficient VRAM, or slower processing speeds. This may lead to a GPU bottleneck and affect the performance of your PC. Our credible bottleneck calculator helps you to find out the best GPU and CPU pairing, so you can have smooth gameplay with stable frame rates.
Signs of a GPU bottleneck
GPU Bottleneck Causes and Solutions
| Cause | Why It Creates a Bottleneck | Recommended solution |
|---|---|---|
| Old/Weak GPU | Can’t handle modern games or high-resolution workloads, causing low FPS and stuttering. | Upgrade to a latest GPU like RTX 3060/4070 or RX 6700 XT/7800 XT. |
| Low VRAM | Limited video memory slows rendering of high-resolution textures and large models. | Choose a GPU with 6GB+ VRAM (8GB+ for 4K or professional tasks). |
| Ultra Settings | Pushing graphics settings to ultra can overwhelm the GPU, causing heat and frame drops. | Reduce graphics settings to High or Medium for smoother performance and upgrade your GPU to handle Ultra settings smoothly. |
| High Resolution | More pixels to render increases GPU workload, reducing FPS. | Lower resolution or use a more powerful GPU. |
| Overheating | Poor airflow or dust causes thermal throttling, lowering GPU performance. | Clean the GPU/case, improve airflow, or upgrade cooling solution. |
| Outdated Drivers | Old or missing GPU drivers reduce stability and performance. | Keep drivers updated using GeForce Experience or AMD Adrenalin. |
3. RAM Bottleneck
A RAM bottleneck occurs when your system does not have enough memory to handle the tasks you’re running at the same time. Since RAM is the workspace where active programs, games, and system processes live, limited memory forces your PC to rely on slower storage like an SSD or HDD, which instantly reduces performance.
When RAM is fully used, your system starts transferring data between RAM and the storage drive. This results in stutters, long loading times, freezes, and poor responsiveness—especially during gaming, video editing, multitasking, or running heavy applications. Even powerful CPUs and GPUs cannot perform properly if they constantly wait for memory to free up.
A RAM bottleneck doesn’t mean your hardware is bad—it means your workload exceeds your available memory capacity. For any GPU and CPU pairing, our bottleneck calculator suggests the best RAM combination for optimal performance.
Signs of a RAM bottleneck
RAM Bottleneck Causes and Solutions
| Cause | Why It Creates a Bottleneck | Recommended solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low RAM Capacity | System runs out of memory for active tasks and starts relying on slower storage. | Upgrade to 16GB for gaming or 32GB for multitasking and content creation. |
| Single-Channel Memory | Limited bandwidth slows data transfer between RAM and CPU. | Install RAM in a dual-channel configuration for better performance. |
| Slow RAM Speed | Lower memory frequency increases latency and delays data access. | Use faster RAM (3200MHz or higher) supported by your motherboard. |
| XMP / DOCP Disabled | RAM runs at default speeds instead of its rated performance. | Enable XMP (Intel) or DOCP (AMD) in BIOS. |
| Background Apps | Unnecessary programs consume RAM needed for games and workloads. | Close unused apps and reduce startup programs. |
4. Storage Bottleneck
Computer storage is where your operating system, software, games, and personal files are permanently saved. Devices like HDDs, SATA SSDs, and NVMe SSDs keep data even when the system is powered off, but their speed directly affects how responsive your PC feels.
A storage bottleneck happens when the drive is too slow to supply data fast enough for the CPU, RAM, or GPU. This often results in slow boot times, long loading screens, delayed file transfers, and sluggish app launches. Traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) are the most common cause because they rely on mechanical parts, while solid-state drives (SSDs) offer much faster access speeds. Our trusted bottleneck calculator analyzes your storage setup and recommends the most suitable option to avoid performance limitations.
Storage Technology Comparison
| Storage Type | Interface / Speed | Optimal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| 5400 RPM HDD | SATA II / 60–100 MB/s | Cold storage, backup archives, large media libraries |
| 7200 RPM HDD | SATA III / 80–160 MB/s | Budget PCs, secondary game or media storage |
| 10K/15K RPM HDD | SAS / 120–200 MB/s | Enterprise servers, databases, high-demand file storage |
| SSHD (Hybrid HDD + Flash) | SATA III / 100–250 MB/s | Laptops and desktops needing balance between speed and capacity |
| 2.5″ SATA SSD | SATA III / 400–550 MB/s | OS drive, budget gaming builds, general applications |
| NVMe Gen3 SSD | PCIe 3.0 / 2,000–3,500 MB/s | Gaming PCs, mid-tier content creation, faster boot times |
| NVMe Gen4 SSD | PCIe 4.0 / 5,000–7,000 MB/s | High-end gaming, 4K video editing, demanding software |
| NVMe Gen5 SSD | PCIe 5.0 / 10,000–14,000 MB/s | Professional workstations, 3D rendering, heavy data workloads |
| Enterprise SSD | PCIe / SAS / 3,500–7,000 MB/s | Data centers, virtualization, high IOPS workloads |
| External USB 3.0 HDD | USB 3.0 / 80–120 MB/s | Portable backups, media transfers, temporary storage |
| External USB 3.2 SSD | USB 3.2 / 400–1,000 MB/s | Mobile workstations, fast backups, consoles |
| Thunderbolt 3/4 SSD | Thunderbolt 3/4 / 2,500–2,800 MB/s | External professional video editing, workstation storage |
| microSD / SD Card | UHS-I / UHS-II / 50–300 MB/s | Cameras, drones, smartphones, portable file transfer |
| Optane / Cache SSD | PCIe / 900–2,400 MB/s | Accelerate slower drives, caching for frequently used apps |
Signs of a Storage Bottleneck
Storage Bottleneck Causes and Solutions
| Cause | Why It Creates a Bottleneck | Recommended solution |
|---|---|---|
| Using an old or slow HDD | Limits read/write speeds, causing slow boot, loading, and file transfers | Upgrade to a faster SSD (preferably NVMe) |
| Low available storage | System and applications can’t cache data efficiently, slowing performance | Free up space or add additional storage |
| Fragmented files on HDD | Files are spread across the disk, increasing access time | Defragment the HDD using built-in OS tools |
| Outdated storage drivers | Old drivers reduce compatibility and slow down data access | Update drivers via manufacturer software (Intel, AMD, or motherboard vendor) |
| Incorrect BIOS storage mode | Using IDE mode instead of AHCI limits SSD performance | Switch BIOS mode from IDE to AHCI for better SSD speed |
| Excessive background disk usage | Other apps (updates, antivirus, downloads) compete for storage I/O | Pause or close unnecessary background applications |
| Slow external storage | External HDD or SD cards have lower throughput than internal drives | Use faster external drives (USB 3.2 / NVMe / Thunderbolt) |
Conclusion
Identifying and fixing PC bottlenecks is key to maximizing system performance. Whether caused by the CPU, GPU, RAM, or storage, etc. Bottlenecks can slow down even with powerful setups. Bottleneck Calculator makes it easy to pinpoint issues and suggest practical upgrades or optimizations. By addressing these weak points, you can ensure smooth multitasking, faster gaming, and unlock the full potential of your PC.
